Page 4 of 6
Correlative HCHO measurements used as a reference for satellite validation are collected from several ground-based monitoring networks contributing to WMO's Global Atmosphere Watch:
- Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) solar absorption spectrometers: About 27 FTIR instruments perform network operation, in the framework of the Network for the Detection of Atmospheric COmposition Change (NDACC), from clean Arctic and oceanic sites to very-high-concentration sites such as Porto Velho, in the Amazon basin.
- Multi-Axis Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy UV-Visible spectrometers (MAX-DOAS): Several of those instruments perform network operation in the framework of the Network for the Detection of Atmospheric COmposition Change (NDACC).
- Direct Sun DOAS UV-Visible Pandora instruments from Pandonia Global Network, currently contributing 30+ instruments.
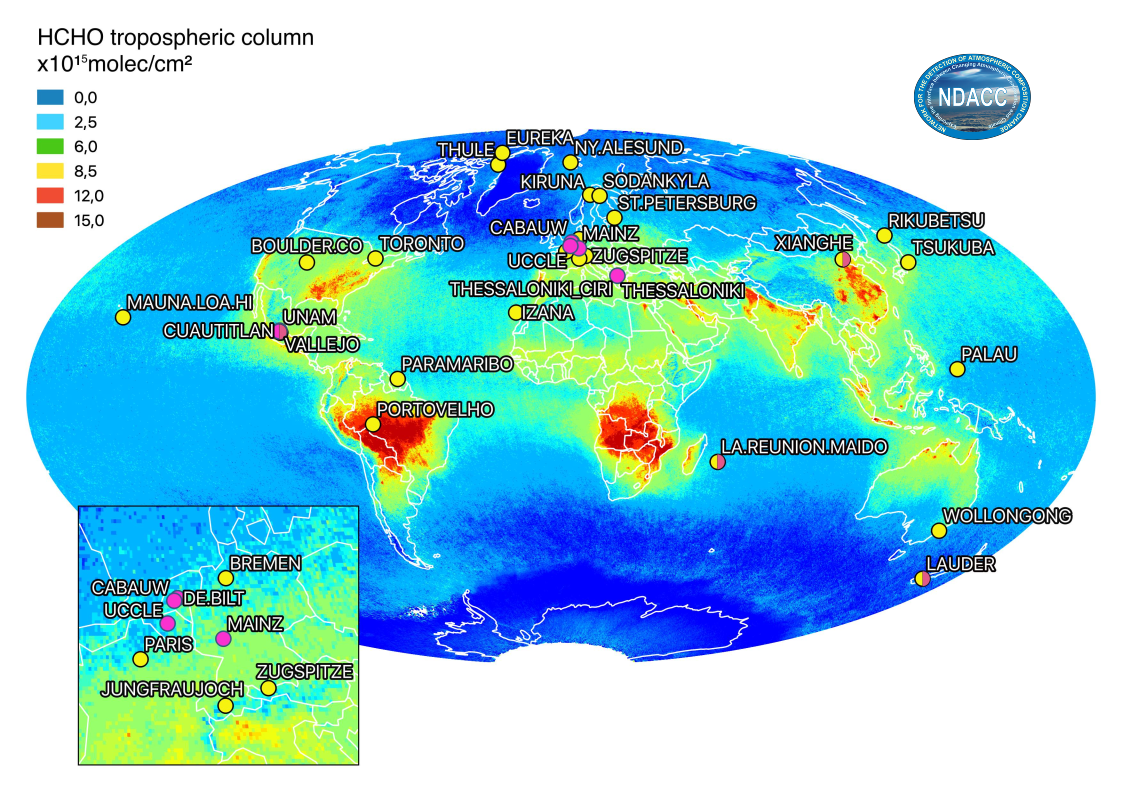
Geographical distribution of the spectrometers contributing HCHO correlative measurements to the validation of Sentinel-5p: TROPOMI: 27 NDACC FTIR (yellow) and MAX-DOAS (magenta). (© Update of Vigouroux et al., AMT 2020).
References
Vigouroux, C. et al. NDACC harmonized formaldehyde time series from 21 FTIR stations covering a wide range of column abundances, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 11, 5049-5073 (2018), doi:10.5194/amt-11-5049-2018
Correlative data is obtained via the following channels:
- S5PVT AO projects CESAR (ID #28596, PI A. Apituley, KNMI) and NIDFORVAL (ID #28607, PI G. Pinardi and C. Vigouroux, BIRA-IASB) for rapid data delivery from NDACC MAX-DOAS and FTIR stations,
- the NDACC Data Host Facility, mirrored at EVDC and at BIRA-IASB for satellite validation purposes.