Validation Summary
The Sentinel-5p TROPOMI L2_NO2 data (tropospheric, stratospheric, and total NO2 column) are in good overall agreement with correlative ground-based measurements (NDACC MAX-DOAS, NDACC ZSL-DOAS, and PGN direct-sun DOAS) and with the OMI QA4ECV NO2 satellite data. Bias estimates meet the mission requirements of <50% for tropospheric NO2 and <10% for stratospheric NO2. For stratospheric NO2, the dispersion estimate meets the mission requirement of <0.5 Pmolec/cm2. For tropospheric Pmolec/cm2 the dispersion estimate exceeds the mission requirement of <0.7 Pmolec/cm2, which can however be attributed partly to comparison errors (irreducible co-location mismatch, and smoothing differences).
| Product ID | Stream | Product | Bias | Dispersion | Special features |
| L2_NO2 | NRTI | NO2 troposphere | -37% | 2.6 Pmolec/cm2 | Bias and dispersion by column amount: Troposphere [<2 Pmolec/cm²] +13 % and [>15 Pmolec/cm²] -40 %. Total [+/-6 Pmolec/cm²]: +6 % / -18 %. |
| NO2 stratosphere | -3% | 0.3 Pmolec/cm2 | |||
| NO2 total | 0±50% | - | |||
| OFFL RPRO |
NO2 troposphere | -28% | 3.1 Pmolec/cm2 | ||
| NO2 stratosphere | -3% | 0.3 Pmolec/cm2 | |||
| NO2 total | -7% | 1.6 Pmolec/cm2 |
Below is an overview of the processor versions for the NRTI, OFFL and RPRO streams.
| Product ID | Stream | Version | Orbits |
| L2_NO2 | NRTI | 02.06.00 | 31751-current version |
| 02.05.00 | 28078-31750 | ||
| 02.04.00 | 24697-28074 | ||
| OFFL | |||
| 02.06.00 | 31705-current version | ||
| 02.05.00 | 28030-31704 | ||
| 02.04.00 | 24655-28029 | ||
| RPRO | 02.04.00 | 2818-24654 |
A detailed description of the method and a comprehensive discussion of validation results can be found in the Sentinel-5p Quarterly Validation Report #21: April 2018 - November 2023
| Latest Quarterly Validation Report | Product info | Current Processor Version |
| #21: April 2018 - November 2023 | See sentinel.esa.int |
02.06.00 |
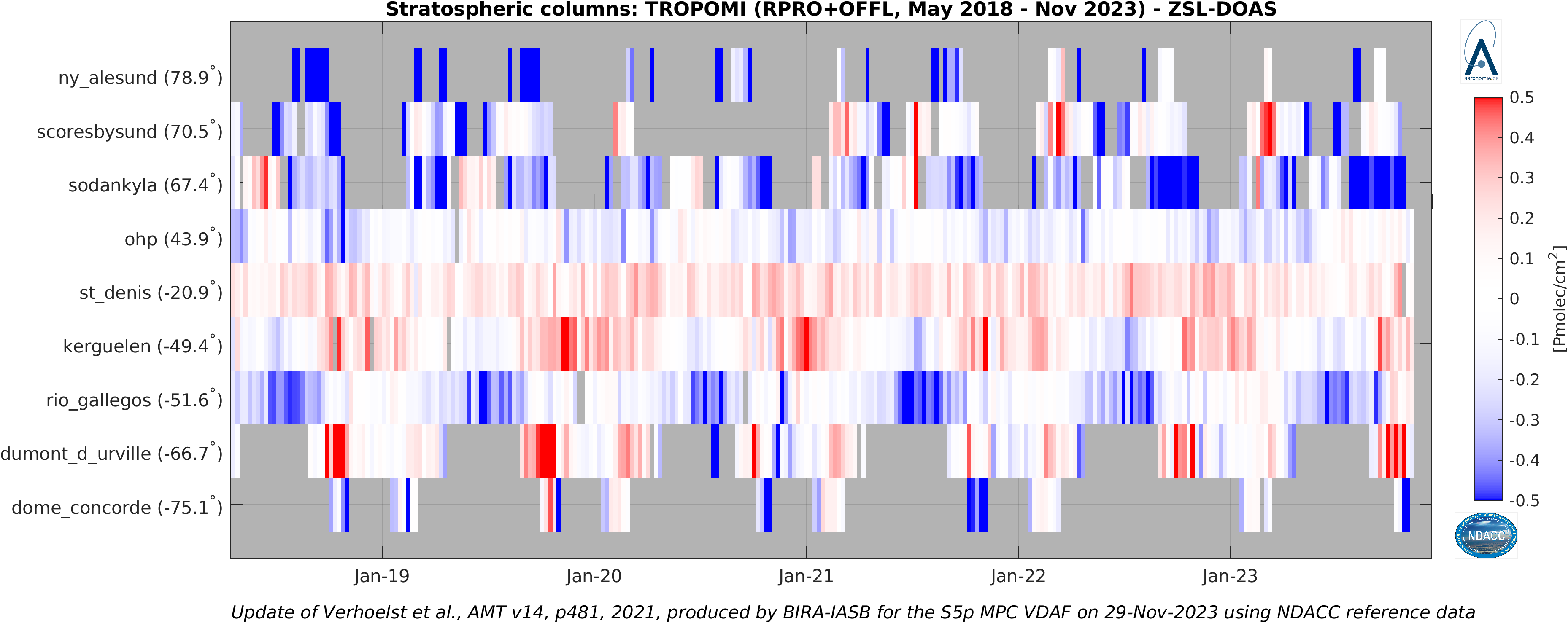
The graph below shows up-to-date time series of the difference between TROPOMI and NDACC ZSL-DOAS stratospheric NO2 column. (© Update of Verhoelst et al., AMT 2021). Stations are ordered by latitude.
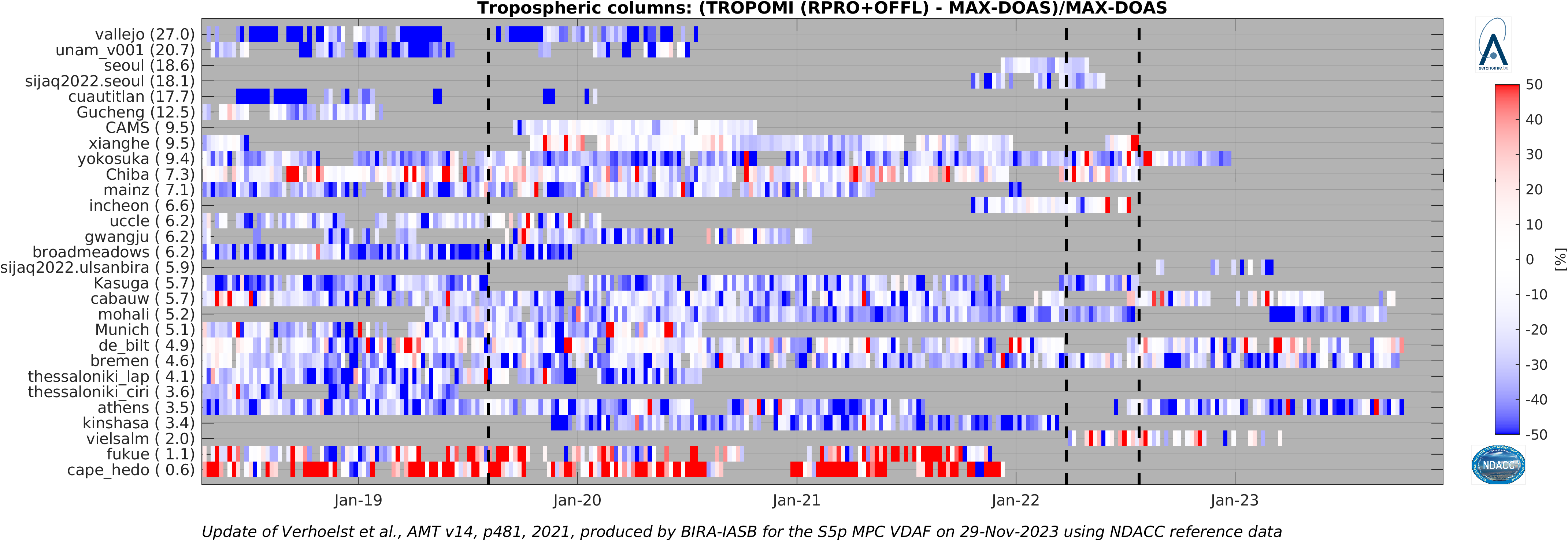
The graph below shows up-to-date time series of the difference between TROPOMI and NDACC MAX-DOAS tropospheric NO2 column. (© Update of Verhoelst et al., AMT 2021). Stations are ordered by median tropospheric column value.
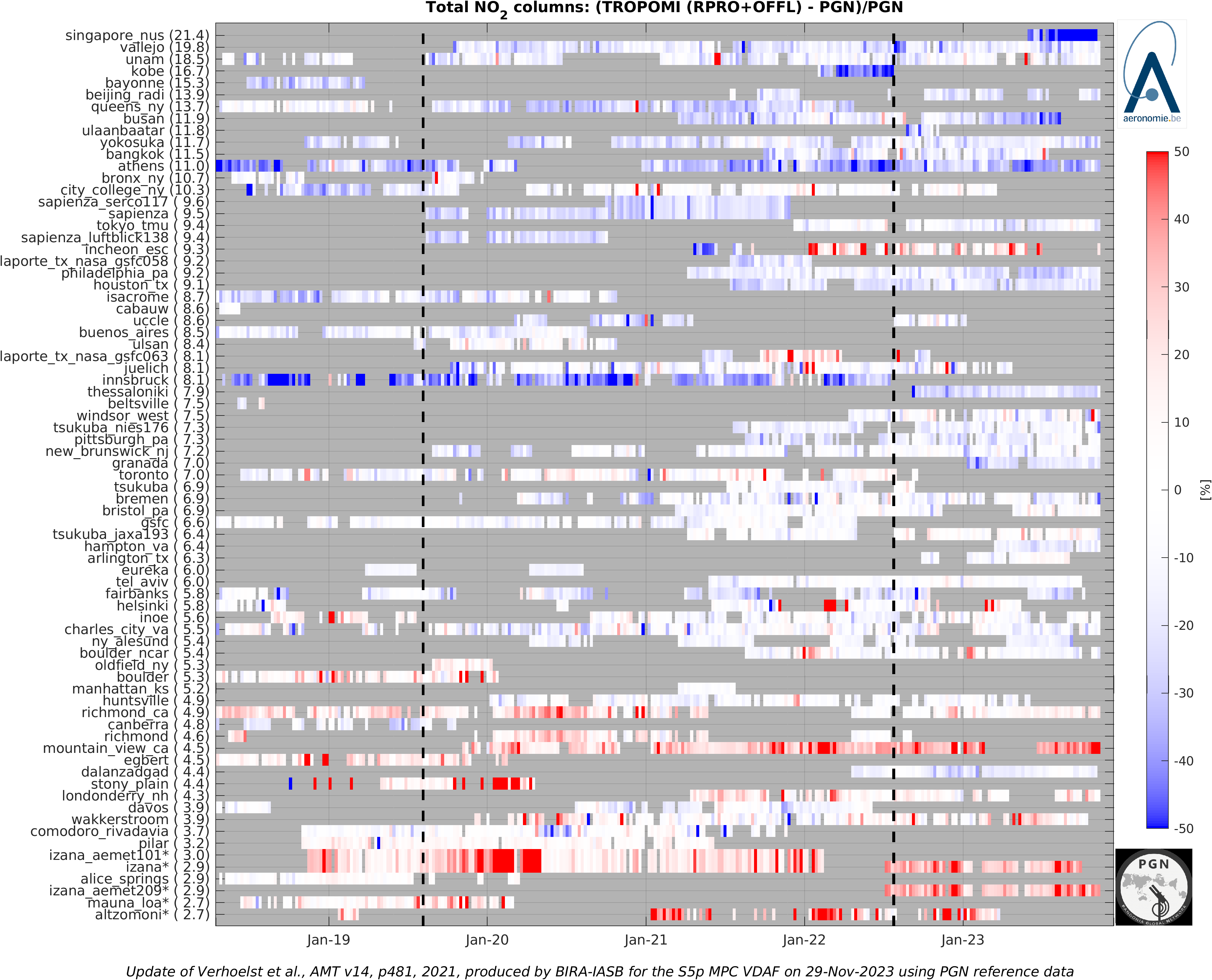
The graph below show up-to-date time series of the difference between TROPOMI and PGN/Pandora total NO2 column data. (© Update of Verhoelst et al., AMT 2021). Stations are ordered by median total column.
The retrieval of Sentinel-5p TROPOMI NO2 data involves the successive determination of three geophysical quantities: the stratospheric, tropospheric and total column amount of NO2. These three quantities are validated as follows:
- The stratospheric NO2 column is compared to ground-based zenith-scattered twilight DOAS measurements (ZSL-DOAS) of the NDACC network. The zenith-sky twilight geometry increases the ground-based sensitivity to the stratosphere. To account for the often large difference in solar local time between the satellite (afternoon) and ground-based (twilight) observations, a diurnal cycle correction is applied based on the PSCBOX 1D stacked-box photochemical model initiated by SLIMCAT CTM fields (Errera and Fonteyn, 2001,Hendrick et al., 2004).
- The tropospheric NO2 column is compared to ground-based multi-axis DOAS measurements (MAX-DOAS). The multi-axis geometry can increase the ground-based sensitivity to the troposphere.
- The total NO2 column is compared to ground-based direct-sun measurements from Pandora spectrometers of the PGN network. Direct-sun measurements are sensitive to the entire column.
Details on the methodology and results are described in Verhoelst, et al. (2021).
Sentinel-5p TROPOMI NO2 data are also compared to alternative retrievals, and to corresponding satellite data from the Aura OMI instrument processed with the QA4ECV community method (Boersma et al., 2018, EC FP7 QA4ECV project).
References
Verhoelst, T. et al., Ground-based validation of the Copernicus Sentinel-5p TROPOMI NO2 measurements with the NDACC ZSL-DOAS, MAX-DOAS and Pandonia global networks, Atmos. Meas. Tech., v14, 2021, p481-510 doi.org/10.5194/amt-14-481-2021.
Errera, Q. and Fonteyn, D. Four-dimensional variational chemical assimilation of CRISTA stratospheric measurements
J. Geophys. Res., 2001 , 106, 12253-12265, doi:10.1029/2001JD900010
Hendrick, F. et al., Retrieval of nitrogen dioxide stratospheric profiles from ground-based zenith-sky UV-visible observations: validation of the technique through correlative comparisons
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 8, 2004, 2091-2106, 10.5194/acp-4-2091-2004
Correlative measurements used as reference for satellite validation are collected from several ground-based monitoring networks contributing to WMO's Global Atmosphere Watch:
- Zenith-Scattered-Light Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy UV-Visible spectrometers (ZSL-DOAS): About 30 ZSL-DOAS instruments perform network operation from the Arctic to the Antarctic, in the framework of the Network for the Detection of Atmospheric COmposition Change (NDACC).
- Multi-Axis Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy UV-Visible spectrometers (MAX-DOAS): Several of those instruments perform network operation in the framework of the Network for the Detection of Atmospheric COmpoisition Change (NDACC).
- Direct-sun Pandora spectrometers, also based on Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy (DOAS), perform network operation in the framework of the Pandonia Global Network (PGN).
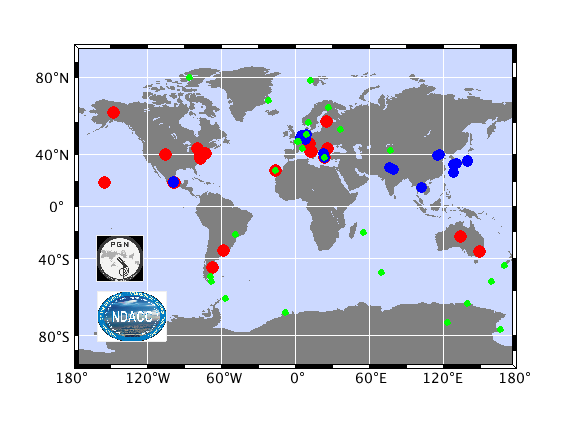
Geographical distribution of the UV-visible DOAS spectrometers contributing NO2 correlative measurements to the validation of Sentinel-5p: 26 NDACC ZSL-DOAS (in green), 19 MAX-DOAS (in blue), and 25 PGN instruments (in red). (© Update of Verhoelst et al., 2021.)
Correlative data is obtained via the following channels:
- ESAs FRM programme and LuftBlick/U. Innsbruck (A. Cede, M. Gebetsberger and M. Tiefengraber) for rapid data delivery from the Pandonia Global Network,
- the SAOZ_RT processing facility at IPSL/UVSQ/UPMC/CNRS LATMOS (A. Pazmino, A. Bazureau, F. Goutail, and J.-P. Pommereau) for rapid data delivery from the NDACC UV-Vis/SAOZ network,
- S5PVT AO projects CESAR (ID #28596, PI A. Apituley, KNMI) and NIDFORVAL (ID #28607, PI G. Pinardi, BIRA-IASB) for rapid data delivery from NDACC MAX-DOAS and ZSL-DOAS stations,
- the NDACC Data Host Facility, mirrored at EVDC and in BIRA-IASB's CORR-2 database for validation purposes,
- the PGN data archive, mirrored at EVDC and in BIRA-IASB's CORR-2 database for satellite validation purposes,
The Sentinel-5p Mission Performance Centre provides an operational validation service relying on the VDAF Automated Validation Server (VDAF-AVS). This fully automated data analysis system collects correlative measurements from quality-controlled monitoring networks and compares them to Sentinel-5p data using community endorsed protocols. It outputs a suite of traceable quality indicators enabling users to judge the fitness-for-purpose of the Sentinel-5p data.
The illustration given hereafter shows the automated comparison of Sentinel-5p TROPOMI total NO2 column data with respect to correlative measurements aquired by a Pandora UV/Visible spectrometer of the Pandonia Global Network. More TROPOMI NO2 validation results are available at http://mpc-vdaf-server.tropomi.eu/no2 .
The VDAF Automated Validation Server in brief:
- hosted at BIRA-IASB and operated with s[&]t,
- provides routine validation for the ESA/Copernicus Sentinel-5p Mission Performance Centre,
- ingests correlative measurements from the ESA Atmospheric Validation Data Centre (EVDC) hosted at NILU, collected from ESA's Fiducial Reference Measurements (FRM) programme and from ground-based monitoring networks contributing to WMO's Global Atmosphere Watch,
- builds on heritage from the Multi-TASTE satellite validation system, the QA4ECV validation server (EC FP7 QA4ECV project) and the CAMS NDACC validation server (EC FP7 NORS project),
- is co-funded by ESA and the Belgian Science Policy Office (BELSPO) as a contribution to the Copernicus Space Component.
Latest Issue
Quarterly Validation Report of the Copernicus Sentinel-5 Precursor Operational Data Products #21: April 2018 - November 2023
Archive
Previous issues of the quarterly validation report are archived here.