Validation Summary
The Sentinel-5p TROPOMI L2_CLOUD data product (Loyola et al., 2018) contains several cloud-related quantities, retrieved with the Optical Cloud Recognition Algorithm (OCRA) and with the Retrieval of Cloud Information using Neural Networks (ROCINN) either with the Cloud-As-Layers approach (CAL) or the Cloud-as-Reflecting Boundaries approach (CRB) (Lutz et al., 2016, Loyola et al., 2010):
- OCRA radiometric Cloud Fraction (CF);
- ROCINN_CAL Cloud Top Height (CTH) and Cloud Optical Thickness (COT);
- ROCINN_CRB Cloud Height (CH) and Cloud Albedo (CA).
The Sentinel-5p MPC performs in routine the following validation checks:
- ROCINN_CAL CTH and derived cloud mean height (CMH) and ROCINN_CRB CH are compared to correlative ground-based measurements from the CLOUDNET and ARM networks;
- OCRA CF, ROCINN_CAL CTH and ROCINN_CRB CH are compared to Sentinel-5p radiometric cloud fraction and cloud height data retrieved with the FRESCO algorithm;
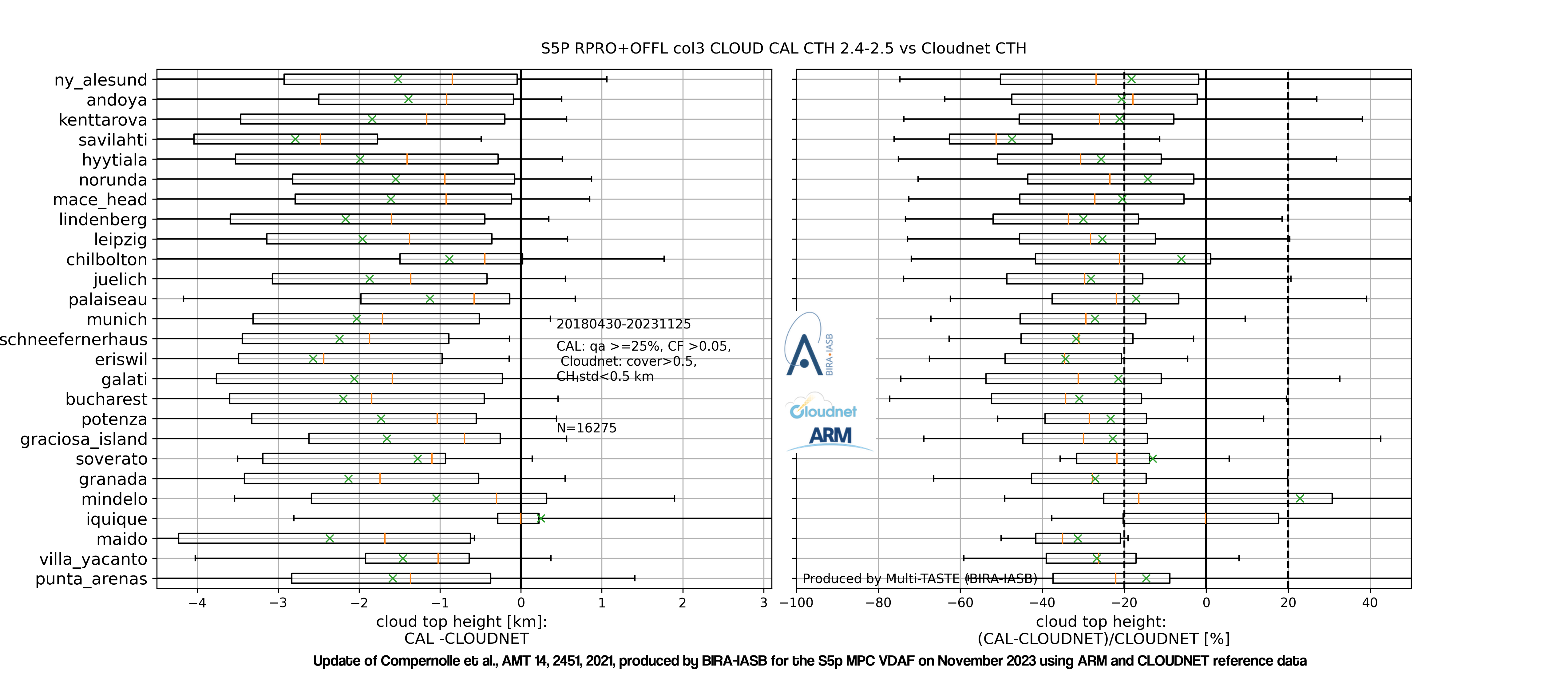
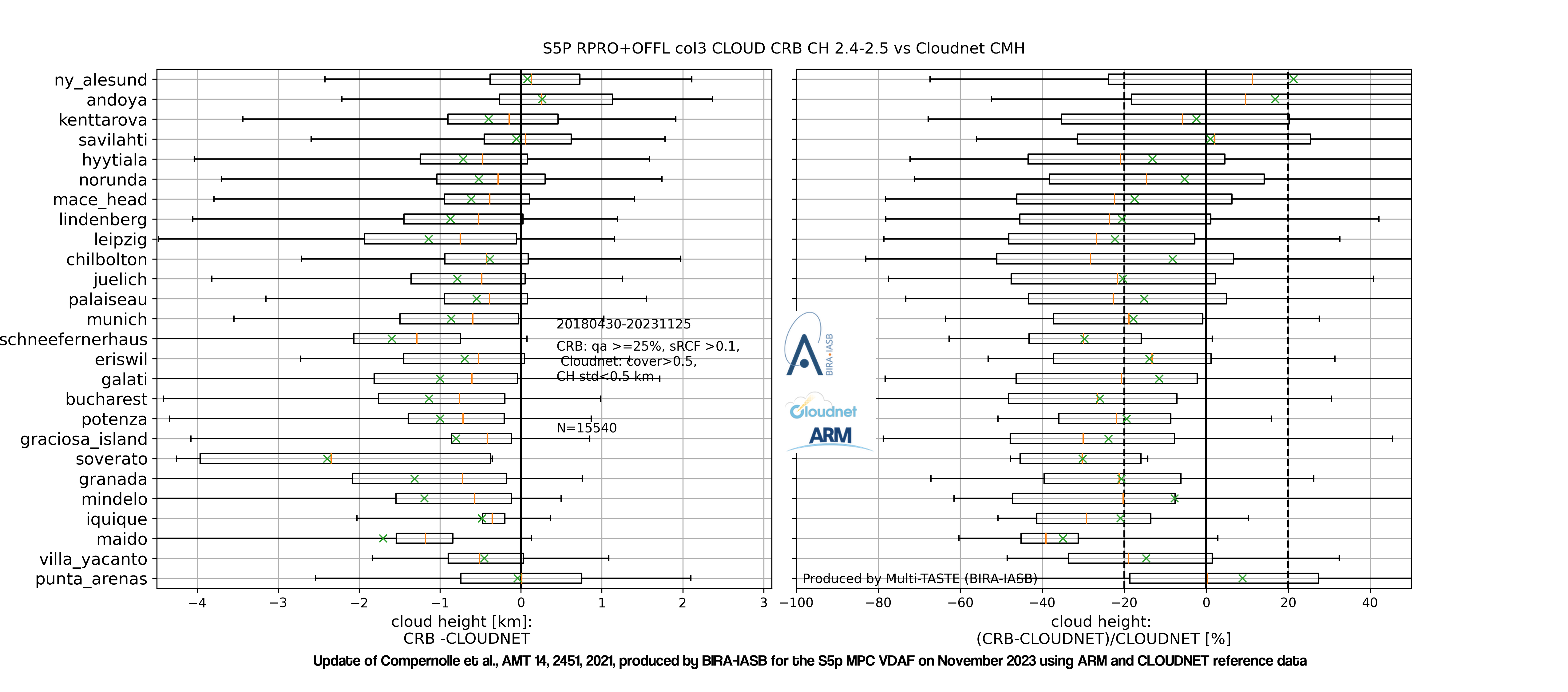
Given their different nature, we look at low (cloud top height below 4km) and high clouds separately. The bias of ROCINN_CAL cloud top height vs. CLOUDNET cloud top height is within the 20% mission requirement for low clouds, but not for high clouds. The bias of CAL cloud mean height vs CLOUDNET cloud mean height is within mission requirements for low and high clouds. The bias of ROCINN_CRB cloud height vs. CLOUDNET cloud mean height is negative and bordering on the 20% mission requirement for high and low clouds. For both ROCINN_CAL and ROCINN_CRB, the dispersion requirement of 0.5 km is met for low clouds but not for high clouds. Given the large difference in sensitivity between the TROPOMI near-infrared observations and the ground-based lidar/radar observations, the agreement is fair.
| Product ID | Stream | Product | Bias | Dispersion | Special features |
| L2_CLOUD | NRTI OFFL RPRO |
CAL CTH (high) | -36% | 1.9 km |
Low clouds: CLOUDNET CTH<4km; high clouds: CLOUDNET CTH>4km. |
| CAL CTH (low) | -15% | 0.5 km | |||
| CAL CMH (high) | -12% | 1.7 km | |||
| CAL CMH (low) | -16% | 0.5 km | |||
| CRB CH (high) | -20% | 1.9 km | |||
| CRB CH (low) | -21% | 0.5 km |
A detailed description of the method and a comprehensive discussion of validation results can be found in the Sentinel-5p Quarterly Validation Report #21: April 2018 - November 2023
| Latest Quarterly Validation Report | Product info | Current Processor Version |
| #21: April 2018 - November 2023 | See sentinel.esa.int |
02.06.01 |
References
Loyola, D. G. et al., The operational cloud retrieval algorithms from TROPOMI on board Sentinel-5 Precursor, Atmos. Meas. Tech. , 11, 409-427, 2018, doi:10.5194/amt-11-409-2018
Lutz, R. et al., OCRA radiometric cloud fractions for GOME-2 on MetOp-A/B, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 9, 2357-2379,2016, doi:10.5194/amt-9-2357-2016
Loyola, D. G.et al., Global patterns in daytime cloud properties derived from GOME backscatter UV-VIS measurements, Int. J. Remote. Sens., 31, 2010, 4295-4318, doi:10.1080/01431160903246741
The graph below shows boxplots of the difference (left) and relative difference (right) between TROPOMI ROCINN_CAL cloud top height and CLOUDNET cloud top height. (© Update March, 2023, of Compernolle et al., AMT 2021). Stations are ordered by latitude. Box edges: first and third quartile; line: median; whiskers: 5 and 95 percentiles; cross: mean.
The graph below shows boxplots of the difference (left) and relative difference (right) between TROPOMI ROCINN_CRB cloud height and CLOUDNET cloud mean height. (© Update March, 2023, of Compernolle et al., AMT 2021). Stations are ordered by latitude. Box edges: first and third quartile; line: median; whiskers: 5 and 95 percentiles; cross: mean.
The Sentinel-5p TROPOMI OCRA/ROCINN retrieval is a two-step algorithm, with two model variants for the second step (ROCINN_CAL and ROCINN_CRB). OCRA computes the radiometric cloud fraction (RCF), ROCINN_CAL retrieves the cloud top height (CTH) and the cloud optical thickness (COT) and ROCINN_CRB retrieves the cloud height (CH, corresponding to the optical centroid) and the cloud albedo (CA).
The different quantities are validated as follows:
- The ROCINN_CAL cloud top height is compared to ground-based lidar/radar CTH measurements of the CLOUDNET and ARM network.
- Similarly, the ROCINN_CRB cloud height is compared to cloud mean height data, derived from the CLOUDNET vertical classification profile data.
- From the ROCINN_CAL cloud top height and the (parametrized) ROCINN_CAL cloud base height, a cloud mean height is derived, and then compared with the CLOUDNET-derived cloud mean height data.
- Several comparisons with cloud parameters of other satellite products are performed: NPP-VIIRS (CTH, COT), Sentinel-5p FRESCO (RCF, CH), Aura OMI O2-O2 (RCF, CH), MODIS (CTH).
Details on the methodology and results are described in Compernolle et al., AMT 2021.
References
Compernolle, S. et al., Validation of the Sentinel-5 Precursor TROPOMI cloud data with Cloudnet, Aura OMI O2-O2, MODIS and Suomi-NPP VIIRS, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 14, 2451–2476, 2021, doi:10.5194/amt-14-2451-2021.
Europe operates a network of ground-based cloud-profiling active remote sensing stations as part of the Aerosol, Clouds and Trace Gas Infrastructure Network (ACTRIS). These stations operate vertically-pointing cloud radar and lidar/ceilometer and use the Cloudnet processing scheme (Illingworth et al., 2007) for the continuous evaluation of cloud profile properties. The Cloudnet scheme combines the cloud radar and lidar measurements at a temporal resolution of 30 s and a vertical resolution of 30 m to create a Level-2 classification product containing cloud base height, cloud top height, and classifications per altitude bin (no cloud, aerosol, liquid cloud droplets, ice cloud, ...). The Cloudnet processing scheme was also applied to similar cloud-profiling measurements from the US Department of Energy Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) sites. Cloudnet products are freely available for download from the Cloudnet database.
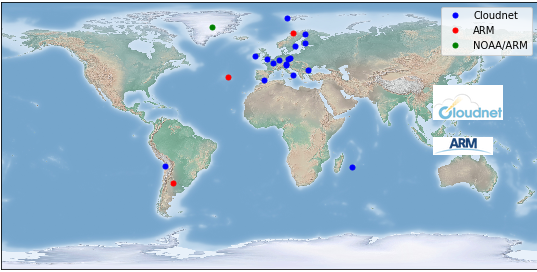
Geographical distribution of the ACTRIS/Cloudnet and ARM instruments contributing cloud (top) height correlative measurements to the validation of Sentinel-5p: CLOUDNET (in blue), ARM (in red), and NOAA/ARM (in green). (© Update of Compernolle et al., 2021/02/18.)
Correlative data is obtained via the following channels:
- the ACTRIS RI and the ACTRIS-2 project (European Commission contract H2020-INFRAIA, grant no. 654109) for providing ground-based data from the Cloudnet sites, produced by the Finnish Meteorological Institute,
- the Cloudnet database, mirrored at EVDC for validation purposes,
- the Atmospheric Radiation Measurement (ARM) user facility, managed by the Office of Biological and Environmental Research for the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science, for providing data for the ARM sites.
References
Illingworth, A. J. et al., Cloudnet, Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc., 88, 883-898 2007, doi:10.1175/bams-88-6-883
The Sentinel-5p Mission Performance Centre provides an operational validation service relying on the VDAF Automated Validation Server (VDAF-AVS). This fully automated data analysis system collects correlative measurements from quality-controlled monitoring networks and compares them to Sentinel-5p data using community endorsed protocols. It outputs a suite of traceable quality indicators enabling users to judge the fitness-for-purpose of the Sentinel-5p data.
The illustration given hereafter shows the automated comparison of Sentinel-5p TROPOMI ROCINN_CAL cloud top height data with respect to correlative measurements aquired by Cloudnet lidar/radar measurements of the Cloudnet database. More TROPOMI CLOUD validation results are available at http://mpc-vdaf-server.tropomi.eu/cloud.
The VDAF Automated Validation Server in brief:
- hosted at BIRA-IASB and operated with s[&]t,
- provides routine validation for the ESA/Copernicus Sentinel-5p Mission Performance Centre,
- ingests correlative measurements from the ESA Atmospheric Validation Data Centre (EVDC) hosted at NILU, collected from ESA's Fiducial Reference Measurements (FRM) programme and from ground-based monitoring networks contributing to WMO's Global Atmosphere Watch,
- builds on heritage from the Multi-TASTE satellite validation system, the QA4ECV validation server (EC FP7 QA4ECV project) and the CAMS NDACC validation server (EC FP7 NORS project),
- is co-funded by ESA and the Belgian Science Policy Office (BELSPO) as a contribution to the Copernicus Space Component.
Latest Issue
Quarterly Validation Report of the Copernicus Sentinel-5 Precursor Operational Data Products #21: April 2018 - November 2023
Archive
Previous issues of the quarterly validation report are archived here.